Table of Contents
LEDs are widely used in various lighting devices, and the development of the LED industry has also accelerated the progress of dimming technology. Dimming technology not only further enhances energy efficiency and extends the lifespan of LEDs but also improves visual effects, enhancing overall quality of life. Silicon-controlled dimming has advantages such as high compatibility, low cost, small size, and easy operation. Currently, there are two mainstream electronic components for achieving dimming: TRIAC (leading edge phase-cut) and MOSFET (trailing edge phase-cut). Today, let’s delve into the discussion about TRIAC dimming.
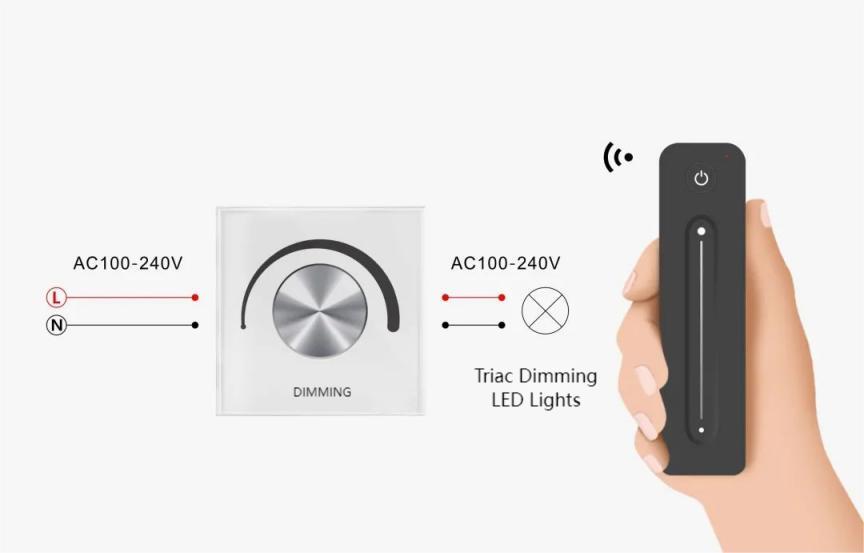
What’s The Triac Dimming?
Triac dimming is a lighting dimming method with physical properties. Its characteristics include not requiring additional signal lines, simple operation, convenient installation, low cost, and the advantage of a long dimming distance. It is suitable for lighting environments dominated by pendant lights, spotlights, and linear lights, often used in places like banquet halls and conference rooms with a 220V AC power supply. Triac dimming has been widely welcomed in engineering. It involves modulating the current supplied to the LED fixture, allowing seamless adjustment of brightness levels. Unlike traditional dimming methods, Triac dimming provides a smooth and precise way to control light intensity, enabling 256 levels of smooth and precise dimming from 0 to 100%. This creates a dynamic and adaptive lighting environment.
This technology utilizes a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) dimmer switch, which is designed to control the power sent to the LED lights by interrupting the AC waveform. The result is a finely tuned lighting experience that can be customized to suit different moods, activities, or occasions.
In essence, Triac dimming in our lights offers a level of control and flexibility that goes beyond mere illumination. It transforms your space into a canvas where light becomes a dynamic element, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Whether it’s creating a cozy atmosphere for relaxation or a well-lit environment for focused work, Triac dimming allows you to tailor the lighting to your specific needs.
The Pros And Cons Of Triac Dimming
Triac dimming technology, as a common dimming method, possesses a range of advantages and some limitations. Here are the main pros and cons of Triac dimming:
Advantages:
High Compatibility: Triac dimming technology exhibits high compatibility across various types of lighting devices and systems, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other dimming technologies, Triac dimming is relatively cost-effective, making it an economical choice.
Compact Size: Triac dimming devices typically have a small footprint, suitable for compact lighting device designs, contributing to space savings.
Easy Operation: Operating Triac dimming devices is relatively straightforward, easy to integrate into various control systems, providing a user-friendly experience.
Disadvantages:
Electromagnetic Interference: Triac dimming may cause electromagnetic interference, impacting the normal operation of other electronic devices, necessitating additional shielding and filtering measures.
Limited Dimming Range: Compared to some advanced dimming technologies, Triac dimming may have a limited dimming range, making it challenging to achieve extremely low brightness levels.
Potential Flicker: At low dimming levels, Triac dimming may produce visible light flicker, which could cause discomfort for certain users.
Potential Power Loss: At certain dimming levels, Triac dimming may be associated with some power loss, leading to a slight reduction in energy efficiency.
Overall, Triac dimming remains an economically viable and effective dimming solution in many applications. However, in scenarios that demand higher dimming performance, it may be necessary to consider employing other advanced dimming technologies.
Why Does TRIAC Dimmming Often Cause Flicker In LED Lamps?

TRIAC dimming, commonly used in traditional incandescent and halogen lighting systems, may cause flicker in LED lamps for several reasons:
Incompatibility with Electronics:
TRIAC dimmers were originally designed for use with incandescent bulbs, which have a different load characteristic than LED lamps. LED lamps are electronic devices, and their internal electronics may not interact well with the phase-cut dimming method used by TRIAC dimmers.
Minimum Load Requirements:
TRIAC dimmers often have minimum load requirements, and LED lamps typically have lower power consumption compared to incandescent bulbs. If the connected load is below the minimum required by the dimmer, it may not function properly, leading to flicker.
Dimmer Design:
TRIAC dimmers are designed to work with resistive loads, and they may not be optimized for the characteristics of LED loads. The rapid switching of the TRIAC can lead to inconsistencies in the LED’s response, resulting in flicker.
Dimming Range:
The dimming range of TRIAC dimmers may not be suitable for the lower power levels of LEDs. At the lower end of the dimming range, the TRIAC may struggle to maintain stable current flow, causing flickering.
Voltage Spikes and Harmonics:
TRIAC dimming can generate voltage spikes and harmonics that may affect the sensitive electronics in LED drivers. This can result in flicker and other undesirable effects.
No Neutral Wire:
Many TRIAC dimmings are designed for installations without a neutral wire. In some cases, this lack of a neutral wire can limit the dimmer’s compatibility with certain LED lamps, leading to flicker.
Quality of LED Drivers:
The quality of the LED driver in the lamp plays a crucial role. Lower-quality LED drivers may not handle TRIAC dimming as effectively, contributing to flicker.
To avoid flicker when using LED lamps with dimmers, it’s recommended to use dimmers specifically designed for LED lighting, such as leading-edge (forward-phase) or trailing-edge (reverse-phase) dimmers that are compatible with the electronic nature of LED loads. These dimmers are designed to address the unique challenges associated with dimming LED lighting sources. Additionally, selecting LED lamps and dimmers from reputable manufacturers with proven compatibility can help minimize flicker issues.
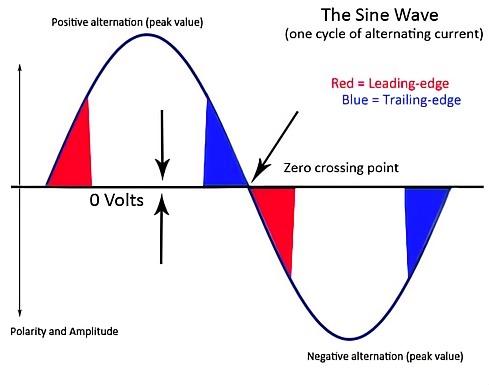
Leading Edge And Trailing Edge Dimming
The two methods differ in the way they control the voltage of the LED lights, which can affect the operation of the dimming.
Leading-edge and Trailing-edge controllable triac dimming refer to the time points at which the control of current conduction and cut-off occurs in a controllable silicon dimming system. Controllable silicon dimming typically utilizes controllable triac devices (such as Triac or SCR) to adjust the current, thereby achieving dimming of the lighting.
Leading-edge Controllable triac Dimming: In leading-edge controllable triac dimming, dimming occurs at the beginning of the positive half-cycle of the current. When the current passes through zero, the controllable triac device is triggered, the conduction angle starts, and the current begins to flow into the light, gradually increasing the brightness of the lighting.
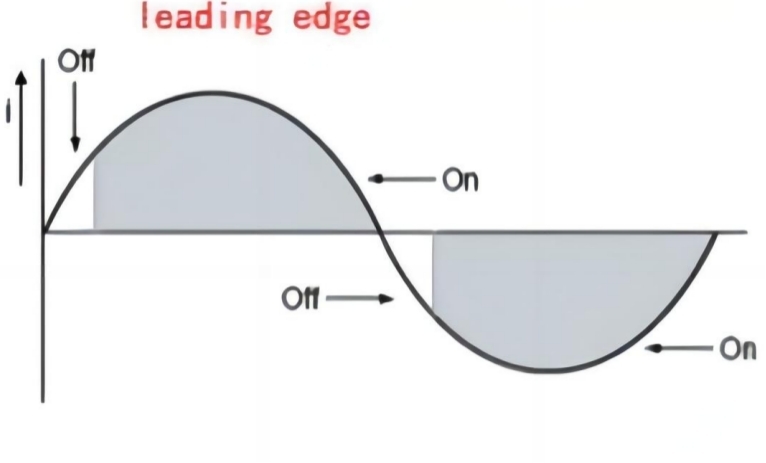
Trailing-Edge Controllable Silicon Dimming: In trailing-edge controllable triac dimming, dimming occurs at the end of the positive half-cycle of the current. When the current passes through zero, the controllable triac device is triggered, the conduction angle starts, and the current begins to flow into the light, achieving a gradual increase in brightness until the end of the positive half-cycle.
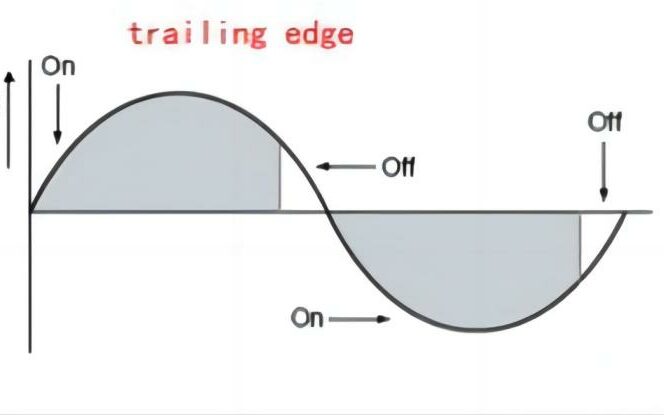
The choice between these two dimming methods depends on specific application requirements and design preferences. Leading-edge dimming and trailing-edge dimming slightly differ in response time and the manner in which brightness changes. Some lighting fixtures or scenarios may be better suited to one method, while others may be better suited to the other.
When selecting leading-edge or trailing-edge controllable silicon dimming, considerations should include compatibility with lighting fixtures, smoothness of dimming, electromagnetic interference, among other factors. Typically, manufacturers specify the dimming method used in product specifications, allowing users to choose based on their specific needs during purchase.
Is Triac A Leading Edge Or Trailing Edge Dimming?
TRIAC dimming can be associated with both leading-edge (forward-phase) and trailing-edge (reverse-phase) dimming, depending on the specific implementation and design of the dimmer. TRIAC dimmers are versatile and can support both leading-edge and trailing-edge dimming methods.
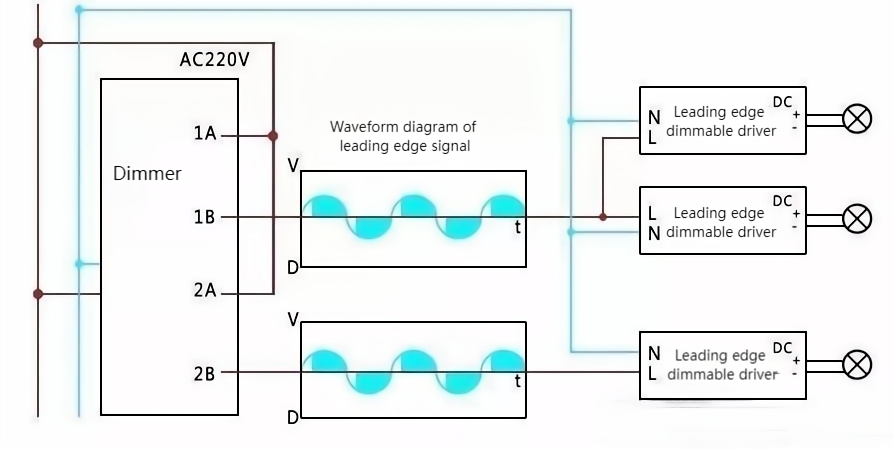
Leading-Edge (Forward-Phase) Dimming:
In leading-edge dimming, the TRIAC dimmer cuts the leading edge of the AC waveform, initiating the dimming process by reducing the voltage at the beginning of each half-cycle. TRIAC dimmers can be designed to perform leading-edge dimming, especially in applications where it is more suitable, such as with certain types of loads.
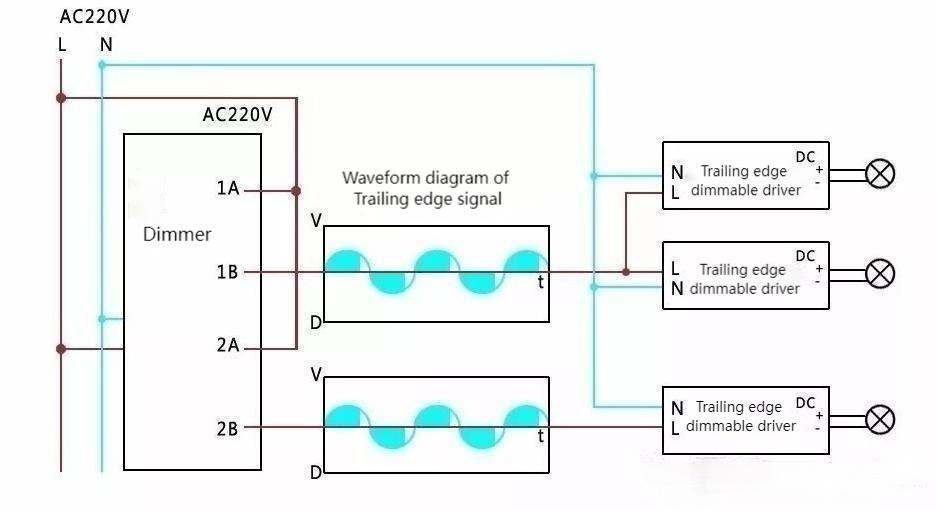
Trailing-Edge (Reverse-Phase) Dimming: In trailing-edge dimming, the TRIAC dimmer cuts the trailing edge of the AC waveform, initiating the dimming process by reducing the voltage at the end of each half-cycle.
TRIAC dimmers can also be designed to perform trailing-edge dimming, which is often preferred for compatibility with electronic loads, including LED lighting.
TRIAC dimmings can support both leading-edge and trailing-edge dimming, and the choice depends on the specific design of the dimmer and its intended application. Some TRIAC dimmers are even designed as “universal” dimmers, capable of accommodating both leading-edge and trailing-edge dimming methods to provide greater flexibility in different lighting scenarios.
Is Leading Edge Dimming Better Than Trailing Edage Dimming?
The choice of the best dimming method for a lighting solution depends on various factors, including the type of light source, the specific application, and individual preferences. There are two primary dimming methods: leading-edge (forward-phase) dimming and trailing-edge (reverse-phase) dimming. Each has its advantages and considerations:
Leading-Edge (Forward-Phase) Dimming:
Advantages:
Generally less expensive.
Often compatible with a wide range of loads.
Commonly used with incandescent and some types of dimmable LED lamps.
Considerations:
May produce audible humming or buzzing sounds.
May have limited compatibility with certain electronic loads, leading to flicker or reduced lifespan in some cases.
Trailing-Edge (Reverse-Phase) Dimming:
Advantages:
Generally smoother and quieter dimming operation.
Often preferred for compatibility with electronic loads, including most modern dimmable LED lamps.
Reduced risk of audible noise.
Considerations:
May be more expensive.
Compatibility with certain loads may vary.
Three factors need to consider:
Light Source Compatibility: Consider the type of light source you are using (incandescent, LED, CFL) and choose a dimming method compatible with that source.
Dimmer Compatibility: Check the compatibility of the dimmer with the specific light fixtures and loads.
Cost: Leading-edge dimmers are often less expensive, but trailing-edge dimmers may offer smoother performance, especially with sensitive electronic loads.
Noise: Leading-edge dimmers may produce audible noise, which can be a consideration in quiet environments.
Recommendation:
For traditional incandescent bulbs, both leading-edge and trailing-edge dimmers are often suitable.
For most modern LED lighting, trailing-edge dimming is generally recommended for smoother dimming performance and better compatibility.
For other types of loads, such as halogen or compact fluorescent lamps (CFL), it’s essential to check compatibility with the specific dimming method.
The best dimming method depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the lighting solution in question. It’s recommended to test dimmers with the specific light sources and fixtures to ensure optimal performance.
How Does Triac Dimming Work In Lighting Solution?
The operation of Triac dimming in light fixtures involves a complex process of current control and regulation. Here is the basic operating principle of Triac dimming in light fixtures:
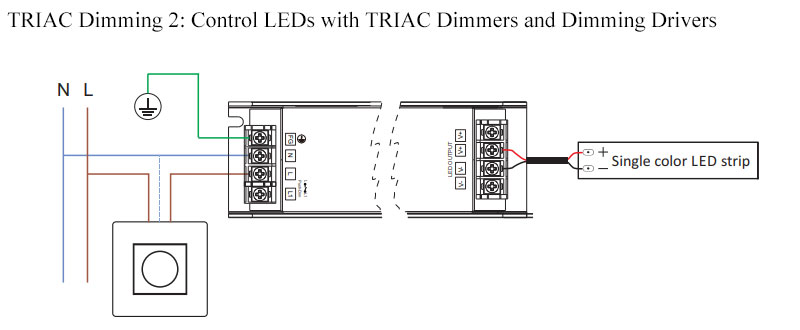
Power Supply: The light fixture initially acquires electrical energy from a power source. This often involves converting alternating current (AC) power into an appropriate direct current (DC) power supply for the LED lights or other lighting components.
Triac Device: The light fixture contains a Triac device, typically a semiconductor device used for current control. The Triac device plays a crucial role in the dimming control within the circuit.
Trigger Angle Control: The trigger angle (also known as the phase angle) of the Triac device determines the conduction time of the current. By adjusting the trigger angle, the conduction time of the current can be controlled, thereby regulating the brightness of the light fixture.
Dimming Control Signal: The light fixture receives signals from the dimming control system, which can come from a wall switch, remote control, or smart home system. These signals instruct the Triac device when to trigger, achieving the dimming effect of the lighting.
Current Adjustment: When the Triac device is triggered, it adjusts the current flowing through the light fixture. By controlling the intensity of the current, the brightness of the light fixture can be adjusted.
In summary, Triac dimming achieves control over the brightness of the light by adjusting the conduction time of the current. This method is a relatively simple and cost-effective dimming technology, suitable for various lighting applications.
Why Dimming Is Needed?
An intelligent dimming system is not just a lighting designer but also a master of scenes. It can create specific scenes in a particular environment, establishing the desired sense of ceremony. Therefore, dimming is often used in upscale hotels, restaurants, conference rooms, lecture halls, and theaters to set the atmosphere, create an intimate feeling, and delight audiences and diners. For everyday home environments, intelligent dimming can both reduce energy consumption and enhance the functionality of the space, creating personalized scenes, enriching lighting modes, and changing from a single tone and layout.

In daily life, the benefits of using intelligent lighting with dimming are evident:
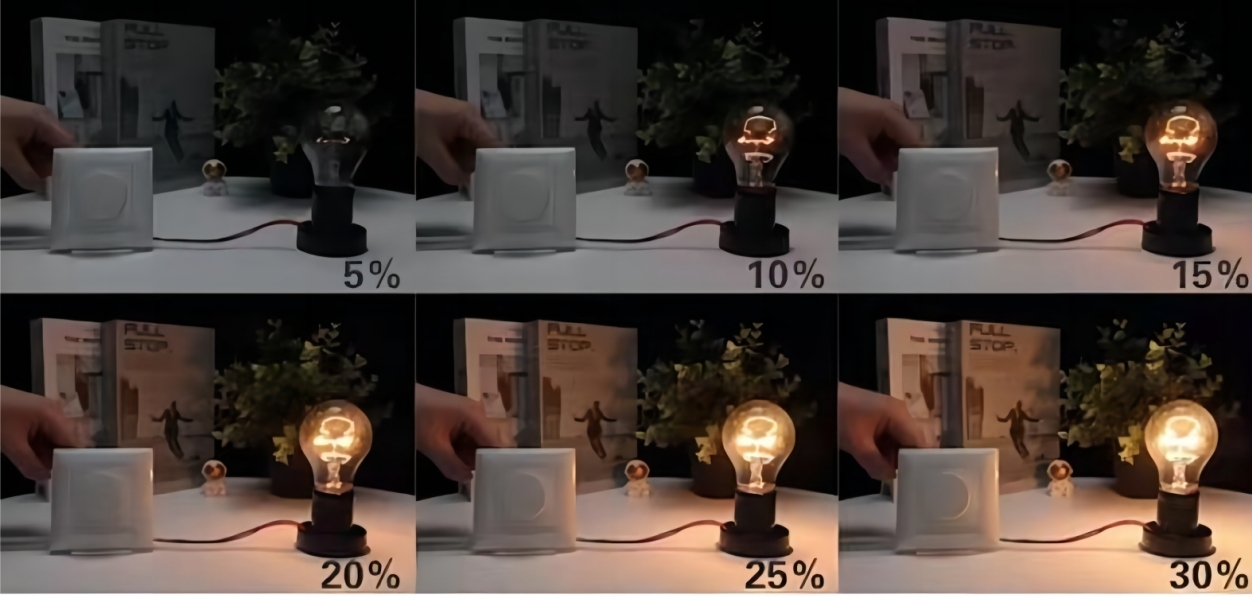
The first benefit: Using intelligent lighting for dimming can improve lighting comfort. The dimming range is from 1% to 100%, and the light transitions gradually rather than abruptly, making it easier for the eyes to adapt. Dynamic changes in color temperature or color create different lighting atmospheres.
The second benefit: Using intelligent lighting for dimming can maximize energy savings. In living or working spaces where natural light is present, light output can be reduced through natural light compensation. In newly installed lighting systems, the design considers the maintenance factor of the lighting system, and the initial light output usually exceeds actual needs by 20%-40%. Dimming saves energy by making full use of natural light, using light-sensitive probes to achieve constant illuminance. When people leave, motion sensors can turn off the lights, and when people enter, the lights can be turned on. When demand is met, manual dimming can be used to reduce output.
The third benefit: Overly bright and flickering lighting can cause light pollution, disturb and harm the human body, causing pupil contraction and increased adjustment, easily leading to eye fatigue and visual impairment.
Four Common Dimming System In Lighting Case.
Smart lighting dimming systems come in various types, we are going to compare different dimming modes, including Triac dimming, 0/1-10V dimming, DALI dimming and Zigbee dimming.
Triac Dimming System: It is a common voltage dimming technology typically used to control the brightness of lighting devices. It utilizes semiconductor devices such as Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) or Triac to adjust the on-off cycles of the current, thereby altering the brightness of the lights.
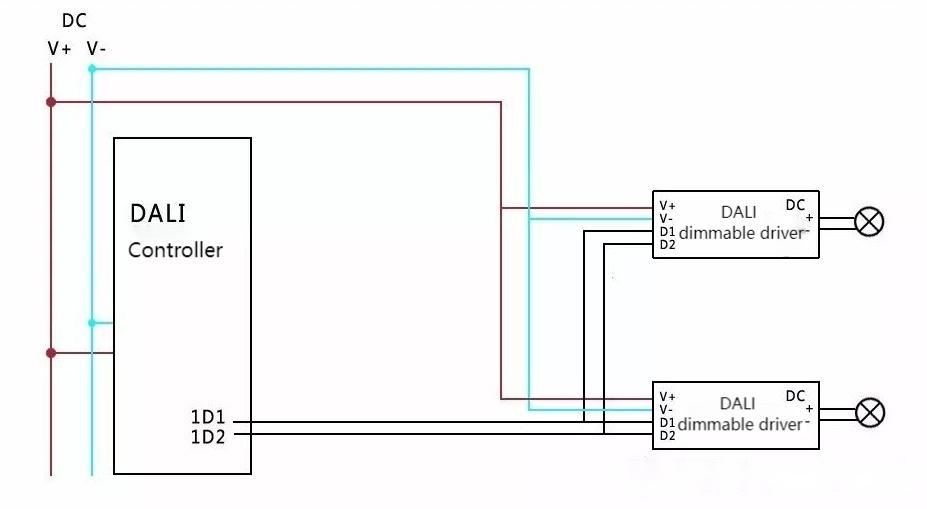
DALI Dimming System: DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) is a specialized lighting control protocol commonly employed in commercial and office settings. DALI dimming systems allow precise control of individual lights, supporting multiple lights and various scene settings.
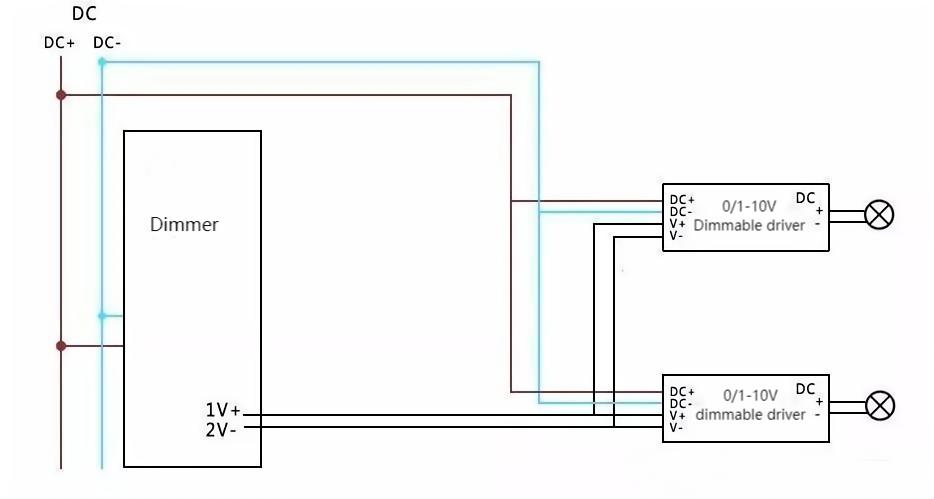
0/1-10V Dimming System: This system uses a voltage range of 0 to 10 volts to control the brightness of lights. This dimming method is widely used in commercial and industrial lighting systems and can also be found in some residential environments.
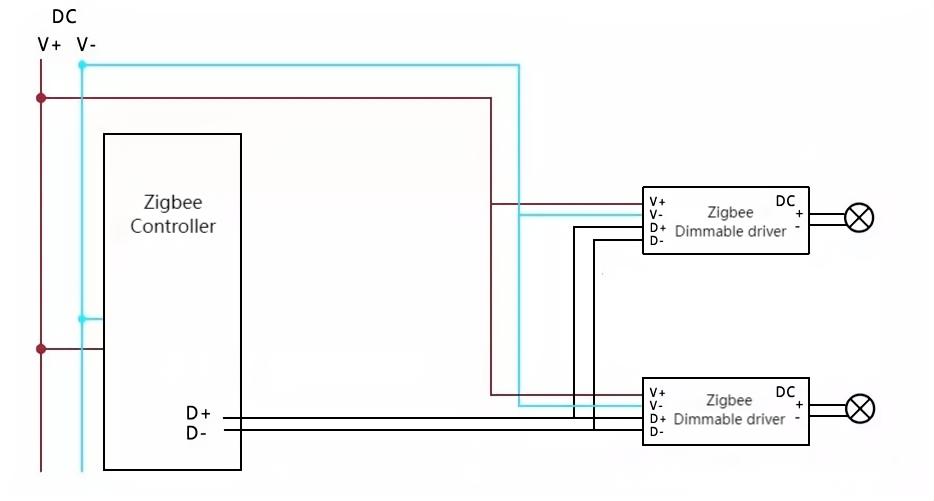
Zigbee Dimming System: Zigbee is a low-power, short-range, low-data-rate communication protocol extensively used in the smart home domain. Zigbee dimming systems can connect to smart home platforms through gateways, enabling remote and intelligent control of lights.
Which Dimming System Is The Best For Lighting Solution?
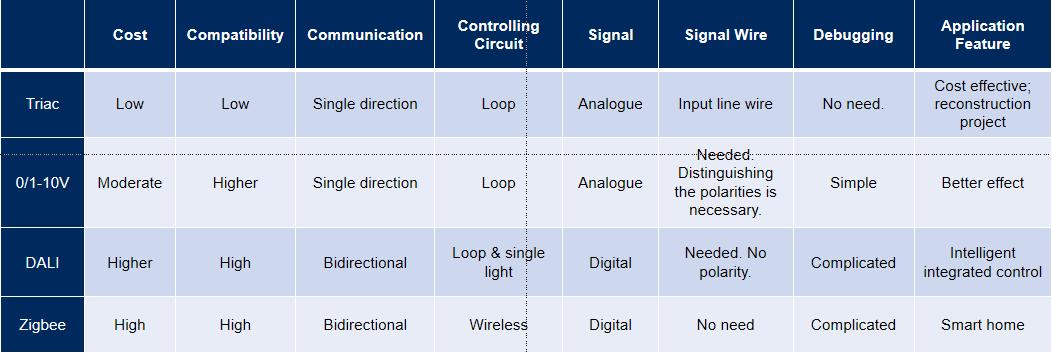
Application Features:
Triac dimming is suitable for reconstruction projects which have the finished light fixtures of Triac dimming installed. If you don’t want to do a lot of work on the reconstruction and don’t have high requirements of the dimming effect, this is a good choice.
Types: Leading-Edge (Forward-Phase) Dimming and Trailing-Edge (Reverse-Phase) Dimming.
Advantages: Cost-effective, widely available, compatible with many types of loads.
Considerations: May cause flicker with certain LED loads, audible noise, and compatibility issues with electronic loads.
0-10V dimming is suitable for the projects that require better dimming effect but with limited budgets. Although it cannot combine light-group control with single-light control, its dimming effect is better than the Triac dimming and it’s with reasonable cost.
Type: Analog dimming system using a 0-10V control signal.
Advantages: Smooth dimming, compatibility with various loads, commonly used in commercial applications.
Considerations: Requires additional control wires, may be more expensive to install.
DALI dimming can be applied to the lighting control of the whole building. Its wired dimming is stable. Meanwhile, it has multiple dimming options, including single-light control and light-group control.
Type: Digital dimming protocol.
Advantages: Individual control of each fixture, two-way communication, suitable for larger commercial installations.
Considerations: Requires DALI-compatible fixtures and controls, may be more complex to commission.
Zigbee dimming is suitable for a smaller system, like smart home wireless control which you use your smart phone to realize a more convenient dimming.
Type: Various wireless protocols (e.g., Zigbee, Z-Wave).
Advantages: Flexible installation, convenient control, suitable for retrofit projects.
Considerations: May require additional devices for compatibility, potential for interference.
Each dimming way has advantages and disadvantages, but suitability is the most important.the best dimming system depends on the specific needs and characteristics of the lighting solution, and it’s essential to consider factors such as compatibility, cost, and control requirements when making a decision. Consulting with a lighting professional can help ensure the chosen dimming system meets the project’s objectives.
Conclusion
In modern society, the pursuit of a personalized living environment is prominent. Traditional lighting effects largely fulfill the basic requirement of illuminating the surroundings. By adopting intelligent dimming solutions, not only can a personalized lighting atmosphere be created, enhancing lighting comfort, but it can also save energy and reduce household expenses. In residential environments equipped with smart dimming systems, various operations and management are extremely convenient. This not only reflects the homeowner’s demands and taste for life but also embodies a lifestyle philosophy that combines technology with environmental consciousness.
Mibang Lighting has been an expert in indoor and outdoor project LED lighting, we can supply lighting design solution to all over the world since 2012. Our dimmable lighting products are with 3C/CE/UL/ETL/ROHS certificates. We have our own lighting products design, our products have warranty for up to 5 years. Contact us today with any project lighting inquiries!
Get Instant Quote
*We respect your confidentiality and all information are protected..




